copyright © 2021 Hope Sandrow all rights reserved

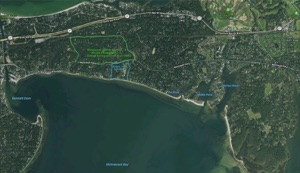
NOW and THEN Shinnecock Hills
The train whistle heard a dozen times a day and more traversing hills once solely First Peoples and their descendants Shinnecock Indian Nation. Who have been bound (since 1859 Note 1) to reservation/territory while their challenge to the claims of Town ownership of more then 4000 acres continues in courts (2016). In what many called a white land grab furthering the interests of the Long Island Railroad and their directors: under the guise of “improvement” the civility of Shinnecock culture, beliefs, practices and Peoples “questioned”, ancestral roots disputed.
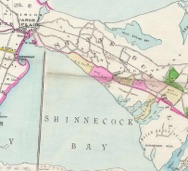
A telescoping story of the railroad’s (Note 2) displacement of native peoples, flora and fauna for purposes of development and gentrification (no information survives detailing LIRR payment for right of way through the Hills, Note 3). The land claim (1859) to the “Hills” named the Trustees of the Freeholders and Commonalty of the Town of Southampton. The Town subsequently sold (1861) the acreage at auction to the newly founded Proprietors of the Shinnecock Hills and Sebonac Sedges. The Proprietors sold rights to the Hills (January 5 1884 for $101,000) to the LIRR subsidiary Long Island Improvement Company, which were subsequently sold privately during the leadership of President Samuel L. Parrish to himself (Note 4), associates, friends and family (above, F. W. Beers Map 1894). A.B. Claflin, J. Romaine Brown, T.G. Condon, LIRR President Austin Corbin, James L. Parrish, Frances K Pendleton. Jane Borrowe Colt (Note 6), Annie Corbin Borrowe, Eleanor Harris Swayne, Helen P. Brown: women exercising their newly won right to own property (Note 5) amidst gains for women’s suffrage. Hill’s landowners (1907) formed the Shinnecock Hills Improvement and Protective Association.
Along with the attraction that artists bring to the narrative: lands gifted to plein air painter William Merritt Chase (Note 7) by Arts Patrons that included Art Museum at Southampton founder and art collector (railroad lawyer) Samuel L. Parrish: for Chase’s Shinnecock Summer School of Art (1891 - 1902) and a home/studio (1891, Architect Stanford White, Note 7). Chase’s conservation efforts, memorialized in his Shinnecock Hill landscape paintings, are mirrored in Sandrow’s art and social practice inspired by her muse the white Padovana cockeral, on ancestral lands, in structures (Note 7) from Chase’s time (1891 - 1914).
The transition of the east end to the Technical Revolution or Second Industrial Revolution (1870–1920) was hastened by train service to the east end: electric power in the early 20th century (1894, Note 8); the first automobile reported (1899, Note 9) in a local newspaper article under one about horse and carriages. Fires burned many Summer “Cottages” to the ground, including the Colt’s (1951): view what “remains”; write a letter in support of preserving these lands, graves (pictured r) from being disturbed. And what “lays bare” unearthed (pictured right, Glass Insulators) from lands that include the Cottage/Carriage House and Carriage/Gatehouse (Note 7) that survived both currently owned by Sandrow/Skogsbergh.
(1892) Completion of the Shinnecock Canal named to memorialize First Peoples (Note 10) ancestral lands, was a matter of local importance to Southampton - then. And now (1975 to present Digital Revolution or Third Industrial Revolution) the environmental impact of new development along its shores of concern to the east end community as well as an element of global dialogue (2006-2016). With “Neighbors”, Sandrow actively opposed a townhouse development along the Canal’s southeastern shores (since 2006, Note 11). Under construction due to the Town’s recent passage (September 8 2020) of legislation protecting sacred ancestral sites and lands despite many decades of promises to Shinnecock Indian Nation. Exploitation and marginalization during the past 160 years activates the work of Shinnecock Nation Graves Protection Warrior Society led by Rebecca Genia; artists Jeremy Dennis, Shane Weeks; Artist and Tribal Attorney Kelly Dennis and Tela Troge.
Threads along a two mile stretch of road in Shinnecock Hills that weave a story of cultural and social history. In which the place of women, community, civil rights, the natural world and “our” nature juxtaposed to art and social history are investigated, as Sandrow’s art practice. And life: (Jan 15 2020) The 38th state voted to endorse the ERA (the first state while Sandrow was in art school March 22, 1972): “Virginia’s decision does not seal the amendment’s addition to the United States Constitution. A deadline for three-quarters, or 38, of the 50 states to approve the E.R.A. expired in 1982.”
Note 1: Shinnecock Nation forced (1859) by an act of the New York State Legislature to “give up” their lands in the Hills that related to a 1703 “lease” with English Settlers. “Shinnecock Hills Long Ago” by Helen M. Wetterau
Note 2: The LIRR eastern tracks to the Hamptons, service to Sag Harbor realized on June 9 1870.“Railroads had been in existence for only nine years when the Long Island Rail Road was chartered on April 24, 1834....There is no doubt that the development of Long Island is directly linked to the growth of its railroad.” MTA Long Island Railroad
Note 3: A timeframe when Sandrow’s great great grandparents and their children suffered the loss of homes and businesses to pogroms, confined to shtetl’s till some escaped to the United States. (Sandrow’s mother’s father) Her grandfather, his parents and siblings immigration memorialized in the words of his first cousin Eliza Greenblatt.
Note 4: Samuel and James Parrish sold (1930) 13 acres along Shinnecock Bay to Lamotte Cohu where he constructed his estate Gissa Bu (pictured, above r). Sandrow’s photographs and research supported the acquisition (2006) for the Community Preservation Fund of ten acres (to where Sandrow followed the white cockeral across the road) in collaboration with Shinnecock Indian Nation. Local history presented in three solo exhibitions: godt tegn (2006-7) PS1/MOMA; (Re)collecting an Americans Dream (2007) Southampton Historical Museum; Platform: Genius Loci (2013-14) Parrish Art Museum.
Note 5: New York legislators passed the Married Women's Property Act in 1848 and the Act Concerning the Rights and Liabilities of Husband and Wife in 1860... most states legislated the rights of women to own property by 1900.
Note 6: The 1894 Beers Map Suffolk County (pictured above) names “Wm M. Colt” as property owner. A 1891 deed for the same property named Jane Borrowe Colt, of which there were two. One, the wife (married at the age of thirteen, 1856) of E. Boudinot Colt, past president of the New Jersey and New York Railway, an Equitable Life Assurance Society Board Director; the second Jane Borrowe was the first named sister’s Mary and her husband Morgan G. Colt’s daughter they named “Jennie Borrowe” who took the name “Jane Borrowe.” (page 27, Jane and Sarah Colt named as owners and page 23 James B. Colt in “Shinnecock Hills Long Ago” by Helen M. Wetterau). Her cousin Hallett Alsop Borrowe - Jane and Mary’s’s nephew - married LIRR founder Austin Corbin’s daughter Anna, their Estate nearby. Jane B/husband E. Boudinot Colts nephew Russell Colt married actress Ethel Barrymore (her initials said to be carved on a Carriage House wooden post) who performed at Guild Hall John Drew (her Uncle) Theatre as did their daughter.
Note 7: (2006) Sandrow titled this project in hommage to Chase’s art practice: (2020) She was informed by neighbor John Hunt to read the Town of SOUTHAMPTON HISTORIC SURVEY that describes her Cottage/Studio: “The structure moved to current location”; “1891; may be carriage house to William Merritt Chase ”. Illustrating that the world is full of chance (or destined?) happenings. “The William Merritt Chase Homestead is listed on the State and National Registers. It is a shingle-clad gambrel-roofed building with a Doric- columned porch. Attached is a shorter, smaller shingle-clad gambrel-roofed structure. It is generally accepted that Stanford White, of the architectural firm, McKim, Mead, & White, made sketches of this
NOW


Google 2020
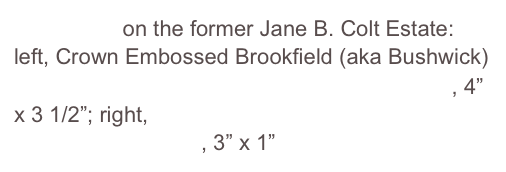


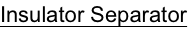
NOW

THEN

(above, left) 1895, Beach grasses, bushes and small trees on gently rolling Shinnecock Hills surround Chase’s home/studio pictured (left,above) in his oil painting Shinnecock Landscape (Note 12) Photograph of Chase’s home/studio from same vantage point as Chase painted but now barely visible through Oak, Juniper, Cedar and Pine trees, many diseased by Eastern White Pine Weevil and Sudden Oak Death. Challenged by thorny thickets of climbing vines (smilax Rotundifolia); sandy soil (to soft to support mature tree height, weight) Photo credit Hope Sandrow
(above) Where Sandrow followed the white Padovana cockeral Shinnecock across the road. l, 1931 photograph by Mattie Edwards Hewitt courtesy Nassau County Museum; Padovana cockeral Shinnecock with Hope Sandrow at Gissa Bu 2006 photo credit Hope Sandrow Gissa Bu;



Note 7 (continued) structure.” Sandrow’s “backyard” includes a Carriage/Gatehouse: “The structure moved to current location: Town of SOUTHAMPTON HISTORIC SURVEY (April 2014 ) Shinnecock Hills Multiple Resource District: “a small gambrel roofed structure clad in wood shingles with dormers, twelve-over- twelve-light windows, and multiple additions. The structure likely dates to the early 20th century. Believed to be the former gatehouse for a larger property known as the Condon Estate (designed by Long Island architect Grosvenor Atterbury ca. 1906); it is also said to have been designed by Grosvenor Atterbury.”
Note 8: “Our village is to have electric lights. A company has been formed, principally of our summer residents...and it is thought the light will be ready for use in a few weeks.” South Side Signal, January 20, 1894 Page 2, Image 2
Note 9: “A special train of the LIRR for horses and carriages will be run on Sept 19, 22, and 26 for L.I. City leaving Amagansett at 6:45 am and stopping at all stations west to Amityille. Horses and carriages should be delivered at least one hour before the train leaves. The first automobile went through this town this week from Southampton to Wainscott. It was owned by James L. Breese. The Corrector, September 16,1899 page 3, image 3
Note 10: From Smithsonian's Handbook of North American Indians: “new tribe‐by‐tribe estimates of North American Indian population size. Collectively these data suggest that population numbered about 1,894,350 at about A.D. 1500. Epidemics and other factors reduced this number to only 530,000 by 1900.”
In 1900: 230,306 native peoples to 75,519,557 non native; in 2019, estimated 2.09% indigenous population of US; 0.24% in New York State.
Note 11: Components of her practice that (again) included organizing neighbors, petitions and photographic documentation. And for the accountability of elected officials: 1 - a lawsuit by the “Neighbors” to appeal the townhouse developments approval by the Town Board (2014); and, 2 - the web based public artwork Sketches of Local History Shinnecock Canal Canoe Place that Sandrow conceived, created, designed. In which Chase’s paintings exhibit the natural world of the canal and surrounding landscape in his time shown as references for area residents to understand the rapid changes since. To feel inspired to envision in a sketch the landscape they want to live in now, including replenishing lands that had been clear cut for development. Tragically (!), that Townhouse development currently under construction due to a replacement Judge (without explanation replaced the first) ruling in the Land Developers and Towns favor to proceed.
Note 12: photo credit Parrish Art Museum
F.W. Beers Map 1894 Atlas of Suffolk County
Hope Sandrow photographed by Nicole Bengiveno (July 15, 2009) New York Times Penelope Green “An Artist Feathering Her Nest”; and
(November 10, 2009) “Lens Blog On Assignment: Fowl, but Photogenic” Artist and subject all rights reserved Nicole Bengiveno


view what remains on the grounds where the Jane B. Colt “Cottage” sited; grave stone “markers” pictured below: write a letter in support of preservation, from being disturbed